Table of Contents
In the realm of industrial automation and control systems, the term “Human Machine Interface” (HMI) emerges as a pivotal component, bridging the gap between human operators and the heart of machinery operations. This blog delves into the essence, functionality, and transformative impact of HMI, drawing insights from Lafayette Engineering’s expertise in the field.
The Essence of Human Machine Interfaces
At its core, HMI is a user interface or dashboard that connects a person to a machine, system, or device. While the concept might seem straightforward, the implementation and impact of effective systems are profound. They serve as the critical touchpoint for operators, allowing for the direct control and management of industrial operations. Operators can communicate with the automation system, input commands, monitor system status, and receive real-time feedback on system performance.
The Evolution and Impact
Historically, the interaction between humans and machines was limited to physical controls and indirect monitoring. However, with the advent of digital technology, HMIs have evolved into sophisticated interfaces that provide comprehensive control and visibility into complex systems. This evolution has not only enhanced operational efficiency but also significantly improved safety, productivity, and decision-making processes within industrial environments.
Lafayette Engineering’s systems highlight several key benefits of HMI programs, including detailed error notifications, status overviews of system areas, and remote access capabilities. These features underscore the importance of HMIs in modern automation systems, where the ability to quickly identify and address issues can have a substantial impact on operational continuity and efficiency.
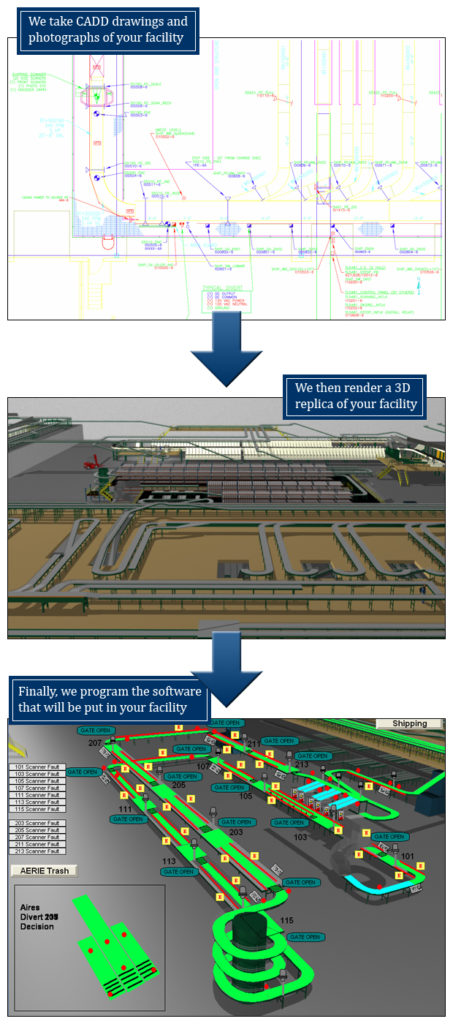
The Technological Advancements in HMI
One of the standout advancements this technology, as noted by Lafayette Engineering, is the integration of 3D drawings into HMI programs. This innovation marks a significant departure from traditional 2D interfaces, offering a more intuitive and accurate representation of complex industrial environments. The use of 3D models facilitates a better understanding of different areas within a facility, enhancing the ability to navigate and troubleshoot systems effectively.
Personalization and Precision
A key aspect of HMI functionality is its adaptability to specific operational needs. Lafayette Engineering emphasizes that each screen can be specifically labeled and personalized for individual facilities. This customization extends to the incorporation of to-scale 3D images, live system statuses, alarm logs, and statistics pages, all tailored to enhance accuracy and efficiency in problem identification and resolution.
The Comparative Advantage
The shift from 2D to 3D HMI interfaces, coupled with the ability to personalize HMI screens, offers a clear comparative advantage. These advancements not only make automated systems easier to operate but also significantly increase productivity within facilities. By providing a more accessible and effective approach to system operation, HMIs empower operators and managers alike, ensuring that they are well-informed and capable of making timely decisions.
The Role of HMI in Engineering Efficiency
The integration of HMI into automated systems is not just about technological advancement; it’s about redefining the efficiency and effectiveness of engineering operations. By facilitating a deeper connection between humans and machines, HMIs play a crucial role in optimizing system performance, enhancing safety protocols, and driving innovation in industrial automation.
Looking Ahead: The Future
As we look to the future, the role of this technology in industrial automation is set to become even more significant. With the continuous advancement of technology, including the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning, HMIs will become even more intuitive, predictive, and user-friendly. The potential to further transform industrial operations is vast, with implications for operational efficiency, system reliability, and the overall human experience in industrial environments.
Conclusion
Human Machine Interfaces represent a critical juncture in the evolution of industrial automation, offering unprecedented control, efficiency, and insight into the workings of complex systems. As demonstrated by Lafayette Engineering, the advancement and implementation of technology are pivotal to the future of industrial operations. By embracing these innovations, industries can look forward to a future where human-machine collaboration reaches new heights of productivity and innovation.
In summary, it’s not just about facilitating interaction between humans and machines; it’s about revolutionizing the way we think about and engage with industrial systems. Through the continued development and application of this technology, we can anticipate a future that is more efficient, safe, and responsive to the needs of both operators and the broader industrial landscape.



